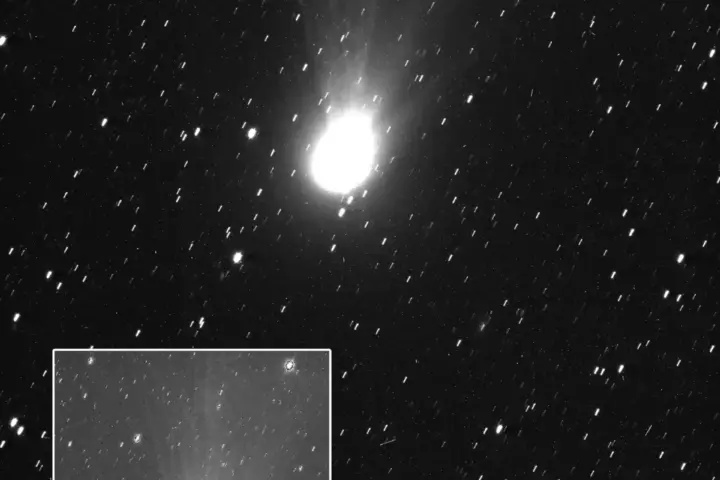
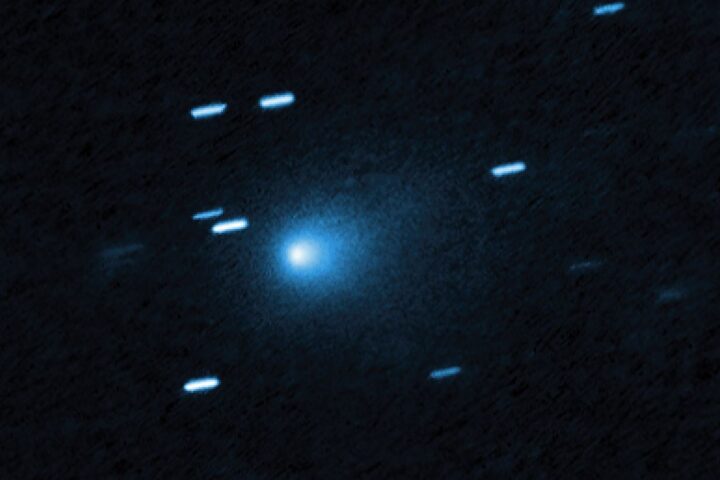
The Comet C/2022 E3 (ZTF) is a rare green comet that has been spotted in the night sky for the first time in 50,000 years and is considered as a rare celestial event. It was first identified in March 2022 and was spotted as a green spot or spec. It hasn’t routed around the Earth or the inner solar system since the last Ice Age. The moment it passed by Earth was in Upper Paleolithic period when Neanderthals were still around. As per NASA, the comet was closest to the Sun on January 12th and it will be visible for the next month. It will be at its brightest on February 2nd, when it comes closest to Earth and can be observed in the constellation Camelopardalis.
Comets are regarded as remnants from the earliest stages of the Solar System’s formation and are composed of frozen gases, dust, and rock. Billions of comets are believed widely to orbit the Sun in the Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud. Comet C/2022 E3 (ZTF) is one of the third space objects found by astronomers during the fifth half-month of the year. It was spotted at the Zwicky Transient Facility and was added to the alphabetical label used to distinguish when objects such as asteroids and comets are discovered. Its closest point to the Sun, called perihelion, on January 12, coming within 160 million km of it.
- Sleep Crisis Looms: Daylight Saving Time 2026 Risks 6% Fatal Crash Spike, Heart Attack Surge
- Katherine Hospital Evacuates as Dual Tropical Lows Trigger Emergency Declaration—467mm Rainfall Recorded
- CrossFit Open 26.2 Live From Cascais: Campbell Wins Duel, CEO Exits, $360 Tickets on Sale March 24
- T-Mobile Promised $200 Gift Cards Per New Line, Then Denied the Deal — Now Faces Class Action
- NOAA G1 Storm Watch March 6: Northern Lights Could Hit 18 U.S. States as Equinox Doubles Aurora Odds
It will keep moving northwest on the horizon throughout January and will be closest to Earth, called perigee around February 1st and 2nd. It will be at a distance of 42 million km from the planet. It will be visible through binoculars in the morning sky somewhere in the Northern Hemisphere during January, and in the Southern Hemisphere in early February. Stargazers can also watch it on YouTube or live streams provided by the Virtual Telescope Project.