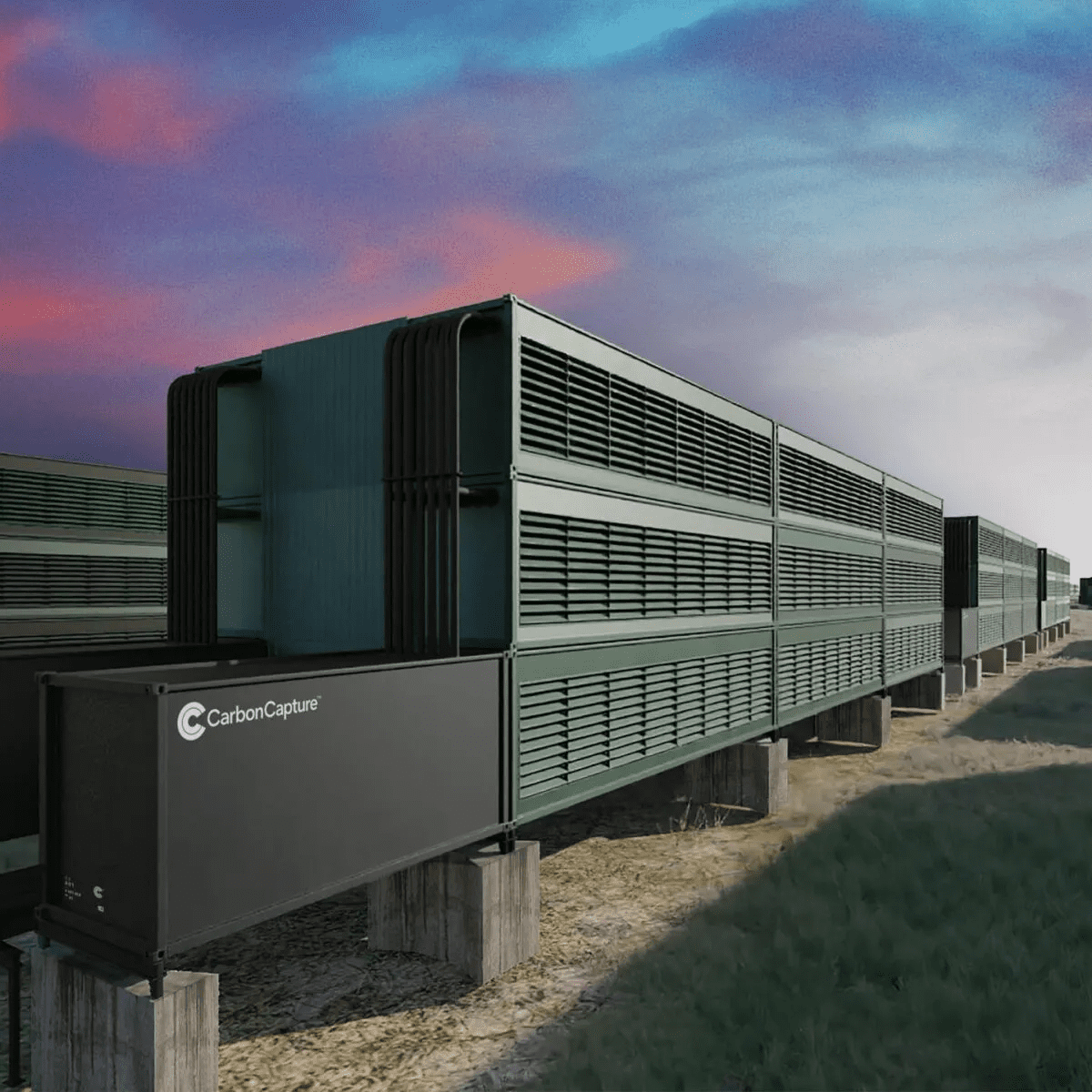
Microsoft has decided to buy carbon removal credits from CarbonCapture, a Los Angeles-based startup. CarbonCapture is setting up a direct air capture (DAC) plant in Wyoming named Project Bison. The DAC plant uses next-generation technology to extract CO2 from the ambient air and move it underground for storage, preventing the greenhouse gas from contributing to climate change.
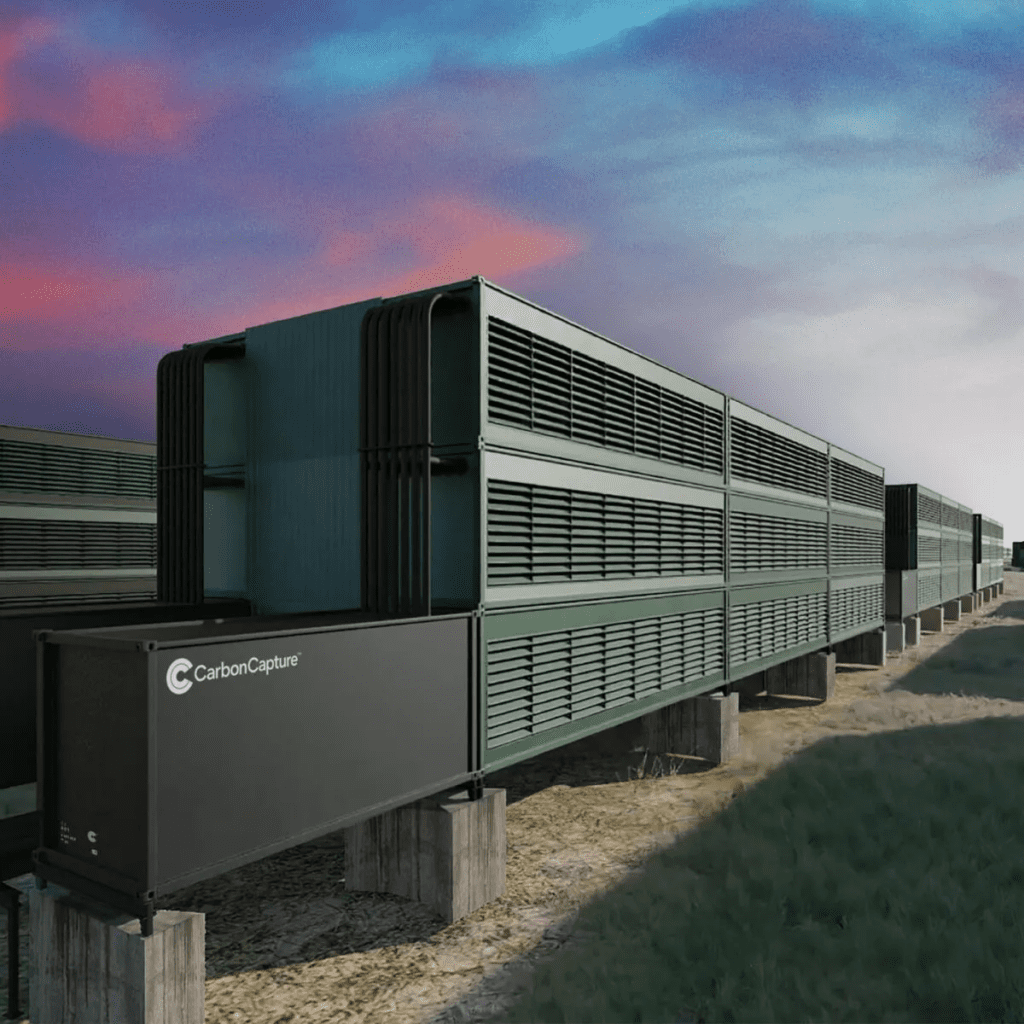

CarbonCapture’s initial modules in Wyoming are supposed to capture and store about 10,000 metric tons of CO2 annually. The industry’s price has been a major limiting factor, with the price per metric ton of captured CO2 sometimes exceeding $600. Microsoft has also procured carbon removal credits from the Swiss company Climeworks.
Carbon removal credits enable companies to offset their carbon emissions by financing carbon capture and storage projects. Microsoft was responsible for approximately 14 million metric tons of CO2 emissions in the fiscal year 2021. CarbonCapture’s deal with Microsoft is bigger than the sum of its deals with other, smaller clients put together. Neither company has given out specific details yet about how much carbon dioxide it wants to remove or how much that will cost.
The market for carbon removal credits is rising as more companies, governments, and investors seek to reduce their carbon footprints. DAC plants have the untapped potential to play an essential role in mitigating climate change by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.