Waymo Targets Detroit for Midwest Launch
Snow-ready upgrades, local data collection, and a pathway to commercial robotaxi service in Michigan.
Introduction
Self-driving cars are headed to the Motor City. Waymo said on Nov. 3 that Detroit has been earmarked for its first Midwestern expansion, supported by a software & sensor update aimed at reliable operation in winter conditions.
Detroiters will see supervised Waymo vehicles on public roads to capture route and environmental data needed ahead of fully driverless service. Waymo has maintained a Michigan footprint since 2016 via its engineering center in Novi, and it assembles and integrates components for the Waymo Driver platform there.
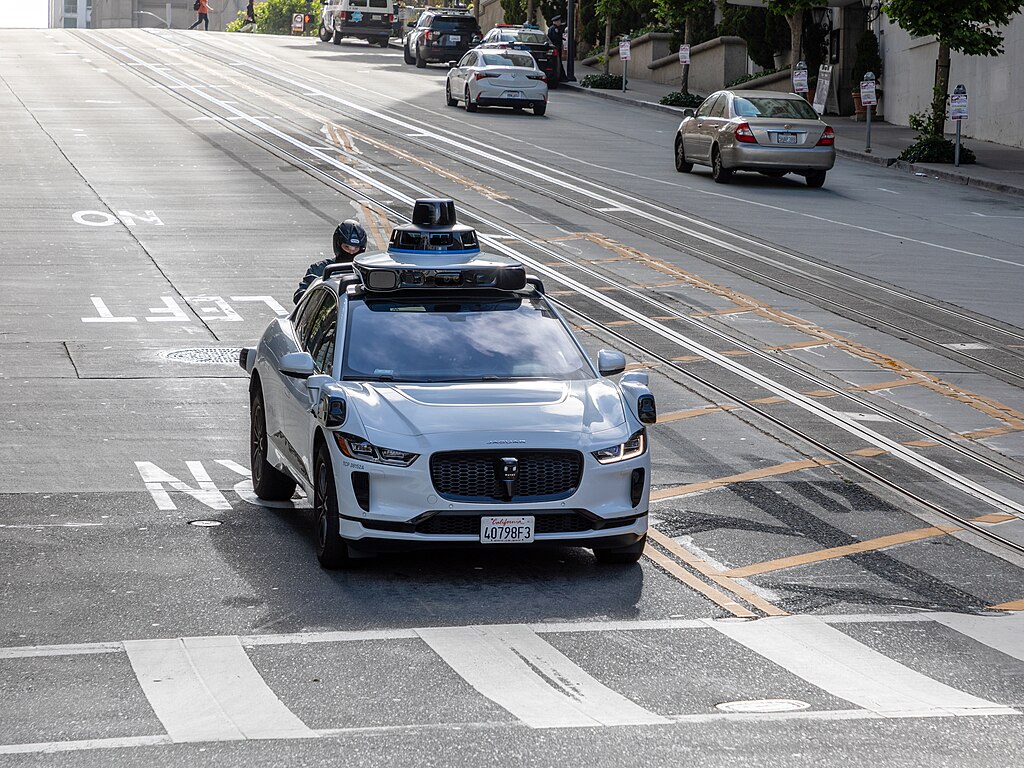
Initial on-road testing in Detroit begins the week of Nov. 3 as the company works toward a regional rollout. Waymo points to extensive winter testing in Michigan and its sixth-generation sensor suite—13 cameras, 4 lidar, and 6 radar—to support operation in snow and low-visibility scenarios.
Related background on autonomous mobility: Karmactive Technology · Karmactive — Mobility

Key Facts
Current U.S. ride-hail markets include San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Phoenix, with broader commercial access continuing to scale. Waymo has reported hundreds of thousands of weekly fully autonomous trips and 100 million+ public-road autonomous miles.
Detroit preparation includes mapping, supervised driving, emergency-services coordination, and state permitting steps prior to serving paid rides. For riders, details on requesting trips appear in Waymo’s ride guide.
What this means
What changes in Detroit right now? Supervised vehicles start collecting local driving data and validating winter behavior. No public driverless rides are enabled until Michigan approvals are completed.
What’s under the hood? Waymo’s 6th-gen stack combines high-resolution cameras with multiple lidar units and radar tuned for rain/snow. The Driver fuses these signals on an onboard compute system for real-time planning.
Conclusion
The update covered Detroit’s selection, supervised testing plans, Michigan facilities, and the sixth-generation hardware details with links to first-hand sources.