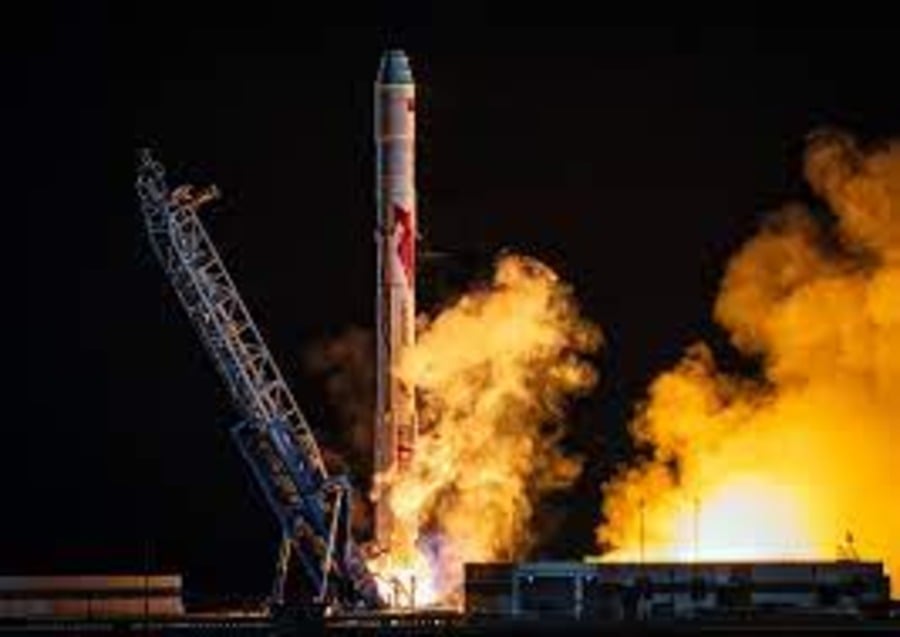
LandSpace, a private Chinese space company, launched its methane-powered rocket on May 17, 2025. The launch from Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center put six satellites into orbit.
The rocket, named Zhuque-2E Y2, marks the fifth flight in the company’s series. What makes this launch special? It uses methane fuel – a cleaner and cheaper option than traditional rocket fuel.
“We expect to test our first reusable rocket in the second half of 2025,” says Zhang Changwu, LandSpace’s founder and CEO. This means the rocket can fly multiple times, which could reduce launch costs.
LandSpace became a world leader in July 2023. They beat major U.S. companies SpaceX and Blue Origin to become the first to successfully launch a methane-powered rocket into orbit.
Similar Posts
The new rocket includes key improvements. For the first time, LandSpace cooled both liquid oxygen and methane below their boiling points. This change boosts the rocket’s thrust.
The launch carried six satellites built by Chinese firm Spacety. These satellites range from 20 kg to 300 kg. The package includes a powerful radar satellite that works in any weather. It can spot changes in Earth’s surface as small as a millimeter – useful for monitoring cities, roads, and buildings.
Li Xiaoming, Spacety’s vice-president, explains the other satellites’ roles. Two will watch Earth’s environment and search for mineral deposits. Three more support China’s deep-space research.
LandSpace’s path shows both success and challenge. Their first launch in December 2022 failed to reach orbit. But they learned quickly. By December 2023, they successfully launched three satellites. Their latest launch now carries six satellites.
Strong financial backing supports their work. In December, they received 900 million yuan ($120 million) from a state-owned fund. This followed their 2020 funding of 1.2 billion yuan ($170 million).

The company started in 2015, just after China opened space flight to private companies in 2014. They’ve grown into a leading private space company, pushing ahead with cleaner fuel and plans for reusable rockets.
Their progress comes with international complexity. Spacety, who made the satellites, faces U.S. sanctions from January 2023 over alleged radar imagery concerns. Spacety denies these claims. This launch proves how fast private space companies can advance. By using methane fuel and aiming for reusable rockets, LandSpace shows how space launches can become more sustainable while potentially reducing environmental impact.