Kidney stone is a painful condition caused due to hard deposits of minerals that form in urine and cause pain when passing through the urinary tract. The occurrence of this condition has risen in the previous 20 years, especially among women and adolescents.
A study in South Carolina, USA was carried out using two different models to gauge the effects of heat associated kidney stone conditions. South Carolina is one of the sunnier regions in the USA.
Roughly one in eleven Americans has suffered from kidney stone disease and these instances have been rising.
The risk of kidney stone disease increases during hotter seasons due to heavy dehydration resulting in concentrated urine and altered urinary flow. Thus higher temperatures due to global warming might lead to a rise in kidney stone patients.
As per the two models used to study the quantifiable rise in kidney stone’s occurrences have two possibilities. If there is an urgent reduction in greenhouse gasses then the cases will rise by nearly 2.2%. And if there is unrestrained release of greenhouse gasses then the cases will spike by 3.9%.
In 2008 Brikowski’s study had indicated that in the USA kidney stone’s disease epicenters from 2000 at 40% will increase to 56% by 2050. The understanding of the disease has moved forward since then and the studies are precisely pointing towards the climate crisis as the impetus.
Scientists believe many other diseases will be triggered and kidney stone’s will remain just one of the many health issues attributable to climate change.
Will Kidney Stone Cases Rise Due To Global Warming?
Latest from Health
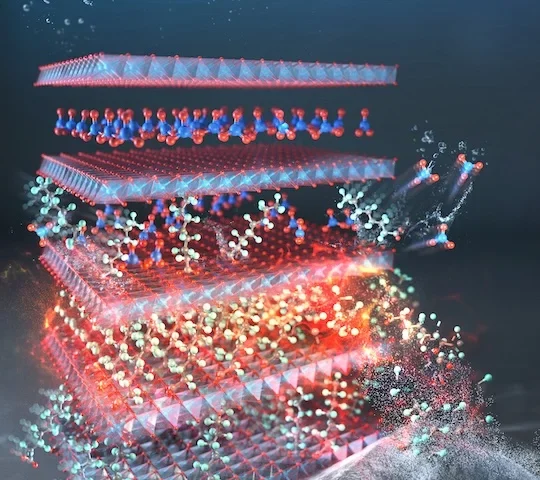
Rice University PFAS removal material captures 1,000× better, works 100× faster than carbon filters — and regenerates itself
Rice University PFAS Removal Breakthrough – Eco-Friendly Technology A copper–aluminum layered double hydroxide material, featured on the cover of Advanced Materials, illustrates the structure used by Rice University researchers to bind and

Phenomenon Studio 2026: Custom Web Development Services That Transform Healthcare Website Design
Key Takeaways I’ve spent the last four years managing custom web development projects at Phenomenon Studio, with particular focus on healthcare website design. Healthcare organizations face a critical challenge: many healthcare websites
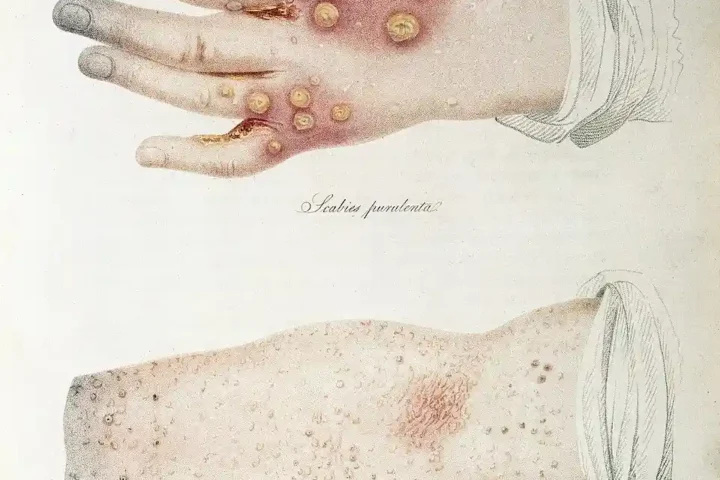
Scabies Surge: 44% Rise Forces UK Into Treatment Crisis As Cases Hit Double Average
Scabies Outbreak UK: Interactive Guide to Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention The Scabies Outbreak: Why Cases Have Doubled in the UK Published January 2026 | Updated with latest surveillance data from the UK

TB Outbreak Amazon Coventry: GMB Union Warns ‘Engine Room’ of Mass Contagion as 10 Workers Test Positive
Amazon Coventry TB Outbreak: Facts, Timeline & Worker Rights Skip to main content TB Outbreak at Amazon Coventry: Facts, Timeline & What Workers Need to Know Understanding the outbreak, the response, and

Air Pollution Crisis: Dutch Engineer Exposes India’s Respiratory Emergency During Wedding Visit
A Visitor’s Health Crisis: The Real Cost of India’s Pollution A Visitor’s Health Crisis: When India’s Pollution Overshadows Promise How two months in India left a Dutch engineer grappling with a pollution

The Ripple Effect Of Financial Stability
Financial stability is often talked about as a personal goal, something you work toward quietly with budgets, savings, and careful choices. But stability rarely stays contained within one person. When finances become
HVAC carbon filter achieves 92.1% efficiency while cutting building energy costs 21.6%
Nanofiber Filter Turns HVAC Systems Into Carbon Capture Devices | KarmActive Nanofiber Filter Turns Building Vents Into Carbon Capture Devices University of Chicago develops filter that captures CO₂ with 92.1% efficiency while

Building a Healthier Narrative
Everyone has a story they tell themselves – about who they are, what they’re capable of, and how life works. Sometimes, those stories empower us. Other times, they quietly limit what we
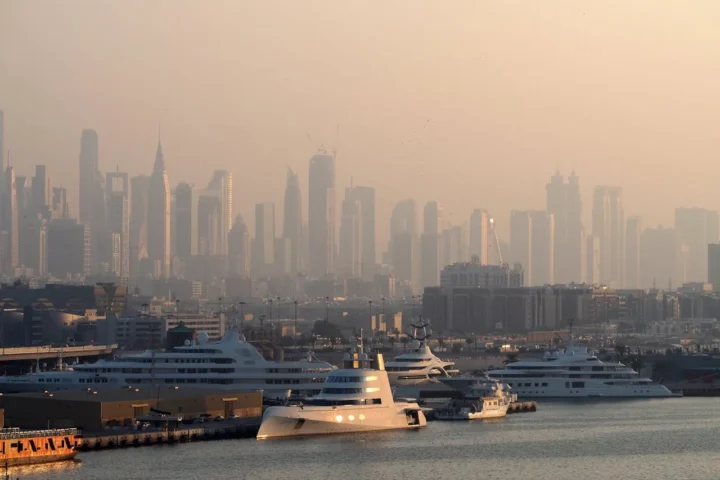

Dubai Ranked #4 Most Polluted Globally As AQI Hits 190+ In 2025 Smog Spike
Dubai’s Air Quality Crisis: What You Need to Know Dubai’s Air Quality Crisis: December 2025 On December 2–3, 2025, IQAir listed Dubai among the world’s most polluted major cities, ranked 4th on
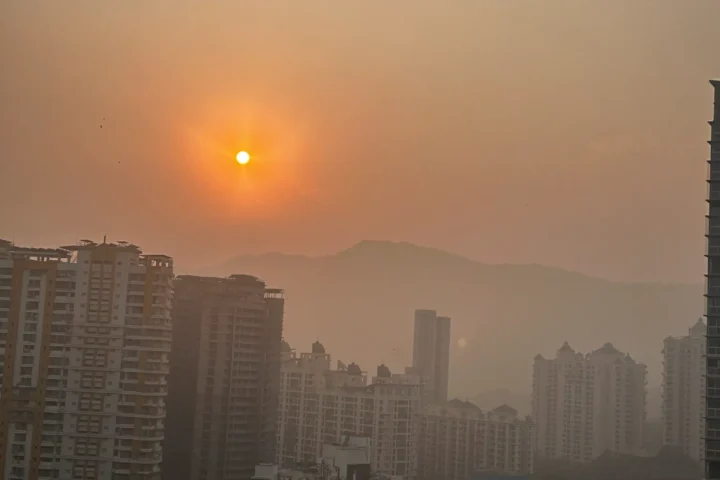

Thane Dust Crisis Rises as 73 Violations Emerge and MSRDC Says “Contractors Will Soon Be Instructed”
Thane’s Dust Crisis: Infrastructure Projects and Air Quality Environment Thane’s Infrastructure Dust Crisis: When Development Costs Clean Air Government infrastructure projects across Thane district create severe dust pollution, raising questions about enforcement
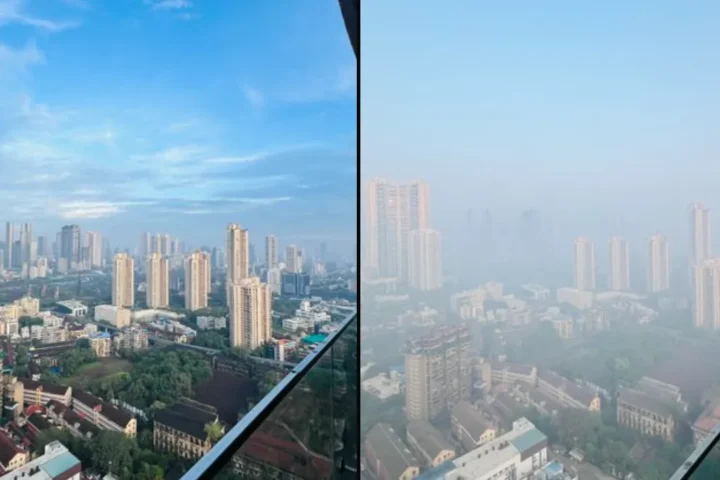

Mumbai Air Crisis (MMR): Why is Maharashtra Government Silent on Public Health Emergency?
Mumbai Air Crisis: Why is Maharashtra Government Silent on Public Health Emergency? GOVERNMENT FAILURE Mumbai Air Crisis: Why is Maharashtra Government Silent on Public Health Emergency? Mazagaon hits severe AQI above 300,

Mumbai GRAP-4: Govt Questioned As 59 Sites Get Notices And Mazgaon AQI Hits 300+ In Worsening Crisis
Mumbai Air Quality Crisis: GRAP-4 Implementation Tracker Mumbai Air Quality Crisis GRAP-4 Implementation Tracker | Real-time Status for MMR Region 🚨 HEALTH ALERT: Air quality worsened across Mumbai – several stations recorded

Harnessing the Power of Vitamins from Natural Sources
Setting the Stage: Why Whole-Food Nutrient Sources Matter Synthetic vitamins are typically isolated nutrient compounds produced industrially, sometimes in forms that are chemically identical to food vitamins and sometimes in slightly different

Ultra-Processed Foods: CDC Says Kids Get Nearly 62% Of Calories; Lancet, WHO Call It A “Systemic Threat”
Global Ultra-Processed Foods Crisis: Interactive Investigation Global Health Emergency Ultra-Processed Foods: The Global Health Threat Hidden in Plain Sight A new three-paper series in The Lancet exposes how industrial food corporations are

Asbestos In Children’s Play Sand: ACCC Recall After TEM Finds Tremolite, “It Was Just By Chance”
Asbestos in Children’s Sand Recall: Facts, Health Risks & Action Steps Health Alert November 2025 Asbestos Found in Children’s Play Sand: A National Recall Explained Schools across Australia and New Zealand closed


