Exposure to higher temperatures is an established threat to public health and has been reported to be associated with many medical conditions and deaths. On extremely hot summer days, US adults are reported to be at an increased risk of visiting emergency dept. (ED) rooms for mental health crises related to substance use, anxiety, stress & more.
This is revealed in a study published in the Journal JAMA Psychiatry by Dr Amruta Nori Sarma and her team at Environmental Health at Boston University School Of Public Health. Amruta and her team obtained daily maximum ambient temperature data from the PRISM climate group. To find the relation between higher temperatures and ED visits, data had to be analysed considering various circumstances including age, sex, locations etc.
Finally the studies suggested established an association between higher ambient temperatures & ED visits. The main findings of the study are as follows:
1. There is a higher likelihood of Emergency Department Visits for mental health conditions on days of extreme heat.
2. This adds to growing evidence that warmth brought on by climate change can worsen symptoms of mental health conditions.
3. The findings could inform Public Health measures to prevent worsening of mental health symptoms in susceptible individuals during high temperatures.
4. The key takeaway from this study is that days of extreme heat are also linked to a higher risk of needing care for mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, substance use & self harm.
5. Extreme weather events such as droughts, wildfires & floods have a clear impact on the mental well- being of the people who experience them.
However, the persistent anxiety about the future of life on our planet looms and can also take its toll. Many environmental campaigners who are frustrated at the failure of politicians and capitalists to act in time to take measures to prevent the adverse effects of climate change on biodiversity as the planet may experience. Thus it is important to build resilience and to turn “eco-anxiety” into positive action.
Man Day Beach Hot Male Ocean Water Drinking
Climate Change & Hotter Weather Can Impact Mental Health – Study Reveals
Latest from Health

CrossFit Open 26.1: 284 Reps, a 12-Min Cap and a 66-Ball Wall Trap Most Athletes Won’t See Coming
CrossFit Open 26.1: The Pyramid That Broke the Gym Floor | KarmActive Sport CrossFit Games competition. Photo: CrossFit Games / Charlotte Foerschler CrossFit Open 2026 CrossFit Open 26.1: The Pyramid That Broke
India Launches Free HPV Vaccine for Girls as Cervical Cancer Kills 42,000 Women a Year — Will 8 Crore Be Covered?
India’s HPV Vaccination Drive 2026 – KarmActive 🛡️ Public Health India • February 28, 2026 India Launches Nationwide Single-Dose HPV Vaccination Drive for Girls Aged 9–14 Prime Minister Modi launches the campaign
Chris Bosh Says “I Went to the Darkness” After Blacking Out — No Warning, No Memory, Wife Called 911
Chris Bosh Says He Woke Up “Covered in My Own Blood,” Reflects on Life After Scare Health & Sport Chris Bosh Says He Woke Up “Covered in My Own Blood” — and

Casey Means Surgeon General Hearing: Vaccines, Pesticides, License Questions
Casey Means Surgeon General Hearing: Vaccines, Pesticides and Ethics Photo: Instagram / @drcaseyskitchen · Oct 24, 2024 Public Health · U.S. Policy Casey Means Faces Senate: Vaccines, Pesticides and Conflicts Questioned in

FDA Class I recall: 55,689 pounds frozen blueberries test positive for listeria in 4 states
FDA Class I Recall: 55,689 Pounds Frozen Blueberries Test Positive for Listeria in 4 States FDA Class I Recall: 55,689 Pounds of Frozen Blueberries Over Listeria Risk ⚠️ HIGHEST FDA RISK LEVEL

Jeriann Ritter reveals bulbar ALS diagnosis after 22 years at WHO 13: “I’m gonna live, and I’m gonna love”
WHO 13 Meteorologist Jeriann Ritter Shares ALS Diagnosis Journey WHO-13 meteorologist Jeriann Ritter holds a personalized scarf gifted by a viewer, a moment from earlier outreach that now contrasts with her disclosure

“Nothing More Than a Glorified Coupon Book” — What Congress Found After Checking TrumpRx’s 43 Drug Price Claims
TrumpRx Drug Price Reality Check Health Policy · Feb 2026 TrumpRx DrugPrice RealityCheck The White House says TrumpRx.gov offers the world’s lowest prescription drug prices. Congressional investigators say nearly half the claims
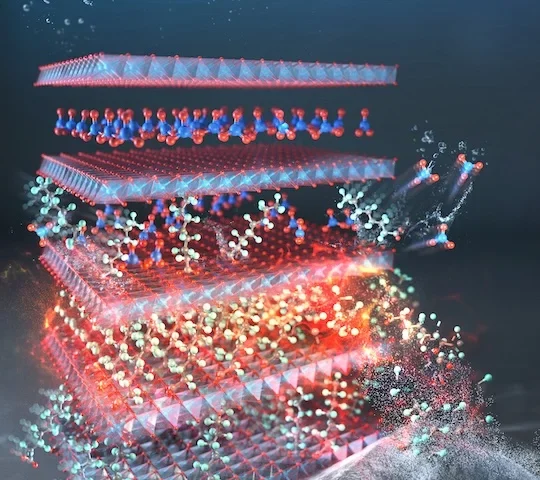
Rice University PFAS removal material captures 1,000× better, works 100× faster than carbon filters — and regenerates itself
Rice University PFAS Removal Breakthrough – Eco-Friendly Technology A copper–aluminum layered double hydroxide material, featured on the cover of Advanced Materials, illustrates the structure used by Rice University researchers to bind and

Phenomenon Studio 2026: Custom Web Development Services That Transform Healthcare Website Design
Key Takeaways I’ve spent the last four years managing custom web development projects at Phenomenon Studio, with particular focus on healthcare website design. Healthcare organizations face a critical challenge: many healthcare websites
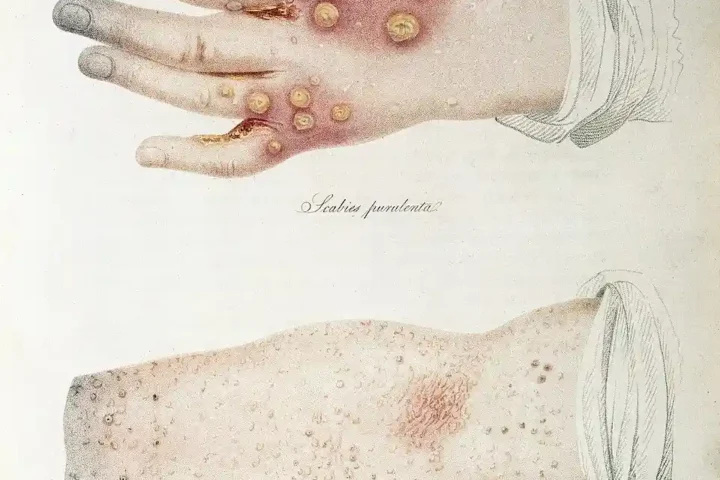
Scabies Surge: 44% Rise Forces UK Into Treatment Crisis As Cases Hit Double Average
Scabies Outbreak UK: Interactive Guide to Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention The Scabies Outbreak: Why Cases Have Doubled in the UK Published January 2026 | Updated with latest surveillance data from the UK

TB Outbreak Amazon Coventry: GMB Union Warns ‘Engine Room’ of Mass Contagion as 10 Workers Test Positive
Amazon Coventry TB Outbreak: Facts, Timeline & Worker Rights Skip to main content TB Outbreak at Amazon Coventry: Facts, Timeline & What Workers Need to Know Understanding the outbreak, the response, and

Air Pollution Crisis: Dutch Engineer Exposes India’s Respiratory Emergency During Wedding Visit
A Visitor’s Health Crisis: The Real Cost of India’s Pollution A Visitor’s Health Crisis: When India’s Pollution Overshadows Promise How two months in India left a Dutch engineer grappling with a pollution

The Ripple Effect Of Financial Stability
Financial stability is often talked about as a personal goal, something you work toward quietly with budgets, savings, and careful choices. But stability rarely stays contained within one person. When finances become
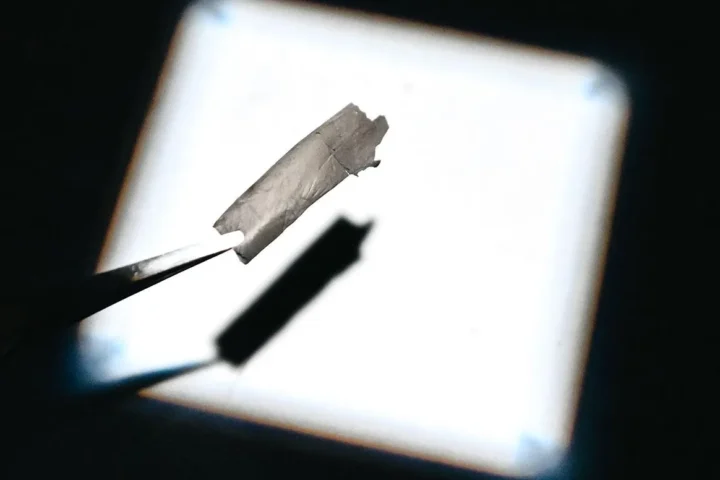
HVAC carbon filter achieves 92.1% efficiency while cutting building energy costs 21.6%
Nanofiber Filter Turns HVAC Systems Into Carbon Capture Devices | KarmActive Nanofiber Filter Turns Building Vents Into Carbon Capture Devices University of Chicago develops filter that captures CO₂ with 92.1% efficiency while

Building a Healthier Narrative
Everyone has a story they tell themselves – about who they are, what they’re capable of, and how life works. Sometimes, those stories empower us. Other times, they quietly limit what we


