China has emerged as the world’s leading energy investor, spending nearly as much on energy as the United States and European Union combined, according to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) “World Energy Investment 2025” report.
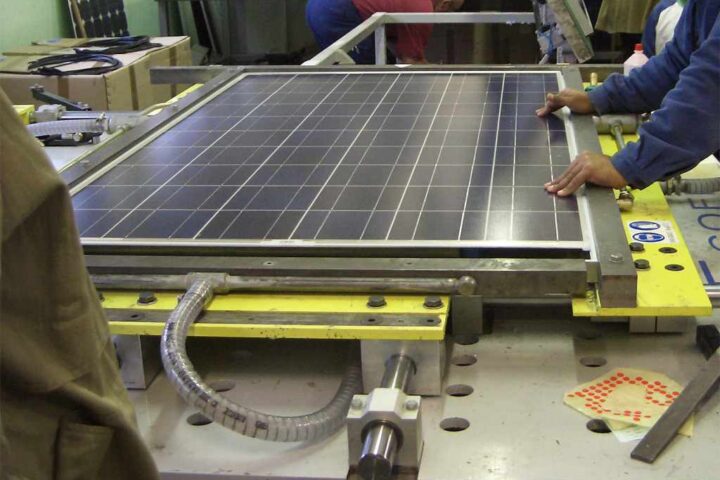
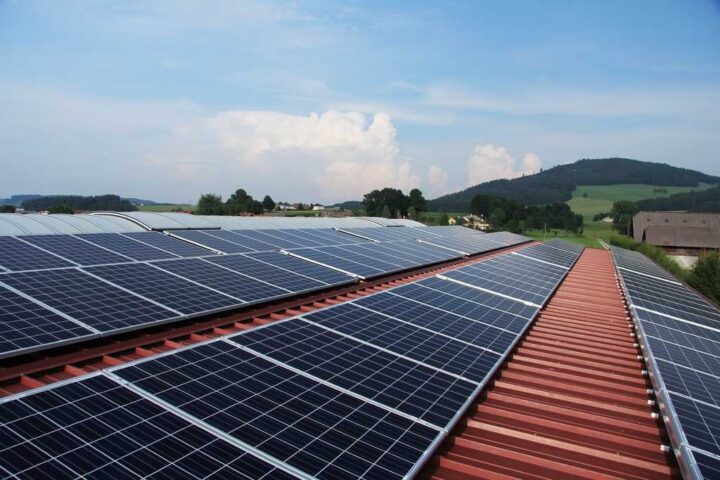
Global energy investment is set to reach a record $3.3 trillion in 2025, with clean energy technologies attracting $2.2 trillion – twice the amount going to fossil fuels. China’s share of global clean energy spending has jumped from 25% to almost 33% over the past decade.
“China is by far the largest energy investor globally, spending twice as much on energy as the European Union – and almost as much as the EU and United States combined,” said IEA Executive Director Fatih Birol.
This dramatic shift represents a major change from just ten years ago. In 2015, China was barely ahead of the United States in energy investment. Today, it has pulled far ahead with strategic investments across solar, wind, hydropower, nuclear, batteries, and electric vehicles.
China’s massive clean energy push isn’t just about fighting climate change. Energy security concerns play a crucial role as countries try to protect themselves from market disruptions and supply problems.
Similar Post
“Amid the geopolitical and economic uncertainties that are clouding the outlook for the energy world, we see energy security coming through as a key driver of the growth in global investment,” Birol explained.
Solar power remains the biggest draw for investment worldwide, expected to reach $450 billion in 2025. Battery storage is also growing rapidly, projected to exceed $65 billion this year, while nuclear power investment has increased 50% over five years to about $75 billion.
The world is moving toward what the IEA calls the “Age of Electricity.” A decade ago, fossil fuel investments were 30% higher than electricity spending. Now, electricity investments are about 50% higher than money spent on oil, gas, and coal combined.

Despite these positive trends, there are troubling signs. Grid investments of $400 billion yearly aren’t keeping pace with new power generation. China also continues investing heavily in coal, starting construction on nearly 100 gigawatts of new coal-fired power plants in 2024.
China’s massive investment in clean energy technologies gives it significant advantages in manufacturing and deploying these technologies at scale. As countries worldwide shift toward renewable energy, China’s early and substantial investments position it to dominate global supply chains for solar panels, batteries, and other critical components.
The question remains whether the US and EU can catch up to China’s head start in clean energy investment or if China’s strategic focus will cement its position as the world’s renewable energy superpower for decades to come.