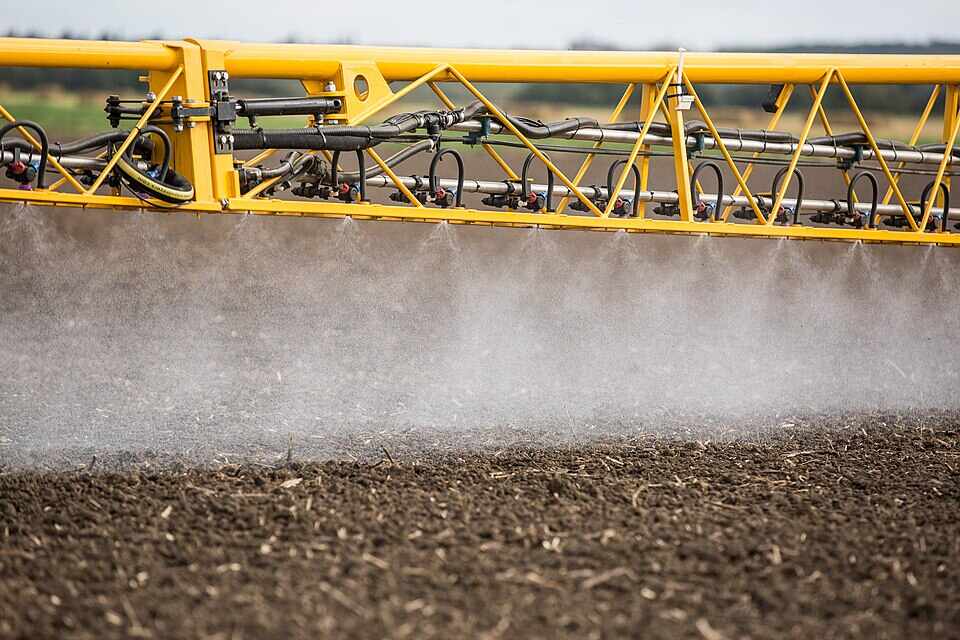
California just took a big step toward pesticide transparency with the launch of SprayDays California, a first-of-its-kind notification system that lets residents know when and where restricted pesticides will be applied near them.
After four years of development, the California Department of Pesticide Regulation (DPR) has created this digital platform that gives advance notice before restricted material pesticides—those subject to the state’s strictest regulations—are used on farms.
“Managing pests—such as insects, rodents and weeds—is vital for protecting public health, the environment, the stability of our food supply and maintenance of our infrastructure,” said DPR Director Karen Morrison. “SprayDays California was developed through extensive public engagement to improve access to information and enhance understanding of California’s strong pesticide regulatory framework.”
How the Notification System Works
SprayDays gives Californians a practical tool to stay informed about chemical applications happening nearby:
- 48-hour advance notice before soil fumigants are applied
- 24-hour notice before other restricted material pesticides are used
- Anonymous map searches or personalized notifications via email or text
- Information on product names, active ingredients, application methods, and treated acreage
- Data presented in one-square-mile sections, matching how applicators report to regulators
The system keeps information available for four days after the scheduled application, accommodating potential weather delays or pest management changes.
Similar Posts
California’s Pesticide Footprint by the Numbers
This new transparency tool arrives as California continues to lead the nation in agricultural pesticide use:
- 209 million pounds applied at peak usage in 2018
- Above 200 million pounds for four consecutive years
- Reduced to 181 million pounds by 2022 (a 5.4% decrease from 2021)
- 17% decrease in fumigant applications between 2021–2022
- 20% decrease in carcinogenic pesticides in the same period
- 56% increase in biopesticide adoption over recent years
Environmental Health Considerations
The chemicals tracked by SprayDays have environmental and health implications:
Water Considerations: Pesticide breakdown products can enter groundwater systems, with CalEPA monitoring in the Tulare Basin showing levels in rural wells.
Greenhouse Gas Factors: Fumigant applications can increase nitrous oxide (N₂O) emissions. N₂O is approximately 300 times more potent as a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.
Pollinator Aspects: Neonicotinoids and pyrethroids used on crops like almonds and grapes affect beneficial insects.
Soil Health Practices
The Healthy Soils Roadmap document identifies several strategies that reduce chemical dependence while building climate resilience:
- Compost application on rangelands can sequester 1–3 tons of CO₂ equivalent per acre annually while increasing forage production by 15–50% even during drought
- Cover cropping reduces nitrate leaching while improving soil structure
- A 1% increase in soil organic matter across California’s 26 million acres of working lands would add 1.5 million acre-feet in water holding capacity
- Organic farming systems typically maintain higher stable soil organic matter than conventional systems
Accessing SprayDays
Residents can access these notifications through the official SprayDays webpage. The platform includes how-to videos and step-by-step guides in both English and Spanish.

For growers and applicators, DPR has created factsheets explaining the new regulatory requirement for electronic submission of Notices of Intent before using restricted material pesticides via the Pesticide Application Notification System Updates.
This system represents a step toward giving communities information about chemical exposures while advancing California’s efforts in pest management.